Home » Articles posted by edplabadmin (Page 2)
Author Archives: edplabadmin
Lab member Mohammadhussein Rafieisakhaei successfully defends Ph.D.!
Our heartiest congratulations to lab member Mohammadhussein Rafieisakhaei for successfully defending his Ph.D. Mohammad’s work focused on motion planning under uncertainty, particularly optimization-based methods. He will continue his research at TAMU.
EDP Lab Wins National Innovation Award @ TCW 2017
Saurav Agarwal and Suman Chakravorty, members of the EDP Lab won the 2017 TechConnect National Innovation Award for the newly developed technology “A Method for Highly Accurate Long-Term Localization and Navigation Using On-Board Sensors.”
This innovation allows a system, such as a vehicle or robot, to navigate autonomously in previously unknown environments with less than a one-meter position error for 100 kilometers of motion without relying on GPS or any pre-built maps. The applications of this technology are immense and include military and commercial use, such as self-driving cars.
The TechConnect National Innovation Award selects the top early-stage innovations from around the world through an industry-review process of the top 20 percent of annually submitted technologies into the TechConnect National Innovation Summit. Rankings are based on the potential positive impact the submitted technology will have on a specific industry sector.
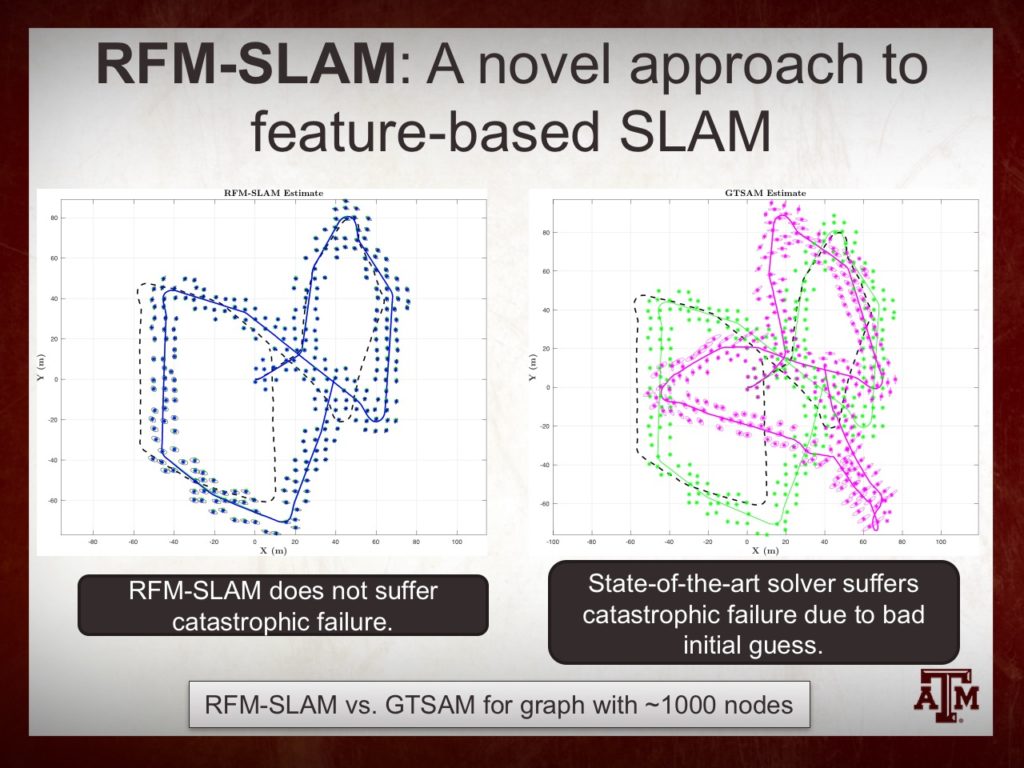
Paper on RFM-SLAM is Accepted to ICRA 2017
Our paper on a novel technique (RFM-SLAM) for 2D feature based SLAM has been accepted to ICRA 2017 to be held in Singapore!
EDPLab Develops a Novel Technique For Feature-Based SLAM
The SLAM problem is known to have a special property that when robot orientation is known, estimating the history of robot poses and feature locations can be posed as a standard linear least squares problem. We have developed a SLAM framework that uses relative feature-to-feature measurements to exploit this structural property of SLAM. Relative feature measurements are used to pose a linear estimation problem for pose-to-pose orientation constraints. This is followed by solving an iterative non-linear on-manifold optimization problem to compute the maximum likelihood estimate for robot orientation given relative rotation constraints. Once the robot orientation is computed, we solve a linear problem for robot position and map estimation. Our approach reduces the computational burden of non-linear optimization by posing a smaller optimization problem as compared to standard graph-based methods for feature-based SLAM. By separating orientation estimation and formulating the robot and landmark position estimation as a linear least squares problem, no initial guess is required for the positions. Further, empirical results show our method avoids catastrophic failures that arise in existing methods due to using odometery as an initial guess for non-linear optimization, while its accuracy degrades gracefully as sensor noise is increased.
[Feel free to study the paper (pdf) submitted for review to ICRA 2017.]
Dan Yu Successfully Defends Her Ph.D.!
Our heartiest congratulations to Dr. Yu on successfully defending! Dr. Yu’s research focused on model order reduction techniques for large scale systems, you may find her publications here. Dr. Yu will continue her research at the EDP Lab.
Decentralized State Estimation via a Hybrid of Consensus and Covariance intersection – Technical Report
This paper presents a new recursive information consensus filter for decentralized dynamic-state estimation. No structure is assumed about the topology of the network and local estimators are assumed to have access only to local information. The network need not be connected at all times. Consensus over priors which might become correlated is performed through Covariance Intersection (CI) and consensus over new information is
handled using weights based on a Metropolis Hastings Markov Chain. We establish bounds for estimation performance and show that our method produces unbiased conservative estimates that are better than CI. The performance of the proposed method is evaluated and compared with competing algorithms on an atmospheric dispersion problem.
Here is a a technical report which is an extended version of the IROS submission with extra proofs and content. TechnicalReport
Saurav Awarded 2015 Roberto Padovani Scholarship From Qualcomm
Lab Member Saurav Agarwal has been selected as one of the winners of the 2015 Roberto Padovani Scholarship for being one of the best performing interns at Qualcomm. The Roberto Padovani Scholarship was created in 2008 to recognize Qualcomm’s corporate research and development interns who demonstrate technical superiority during summer internships. The scholarship is named for Roberto Padovani, who was Qualcomm’s chief technical officer for almost a decade and who was a leading innovator of the company.
Candidates for the scholarship are nominated by their mentors or managers at the end of the internship. The nomination then must receive support from Directors and VPs after which the VPs in the organization meet and select the recipients from the pool of candidates.
Saurav’s research at Qualcomm was in the area of Simultaneous Mapping and Planning for Aerial Robots using Vision Based Sensing. His efforts focused on developing algorithms and implementing them on real hardware using Qualcomm technology to create the next generation of autonomous UAVs.
During his internship at Qualcomm, Saurav and his mentor (EDPL Graduate Dr. Ali-akbar Agha-mohammadi) filed 6 inventions for the new technology they created. They hope to demonstrate the results of their research in the coming months.
The 8 recipients of this year’s scholarship each receive a $5,000 academic scholarship. If a student chooses to come back as a second-year intern or as an employee in the future, then he or she is eligible to receive a generous return bonus.
Lab member Saurav Agarwal will be at Qualcomm Research
Lab member Saurav Agarwal will be interning at Qualcomm Research in San Diego for the summer and fall of 2015 where he will work on autonomous vision-based navigation for micro aerial vehicles.
Feedback-based Information RoadMaps with Open Motion Planning Library
We are pleased to announce that the developers of OMPL (Open Motion Planning Library) at Rice University have posted a guest article by our lab on our latest work on integrating FIRM with OMPL. We would particularly like to acknowledge the support of Mark Moll in this process. Feel free to browse our code on Github and use it in your motion planning research.
Link to Blog: http://ompl.kavrakilab.org/blog
Link to Facebook post: https://www.facebook.com/pages/OMPL/320018418039567